Cap and Neck Finishes
A container’s neck finish holds the cap, stopper, or closure with protruding threads. A container and its corresponding cap must have matching finishes. For example, a 24/400 bottle will only accept a 24/400 closure.Screw thread or continuous thread closure sizes are expressed with two numbers separated by a hypen or slash. The first number refers to the millimeter diameter measured across the inside of the cap’s opening or the outside of the bottle’s threads. The second number refers to the thread style, “GPI” or “SPI” finish. The Glass Packaging Institute (GPI) and Society of the Plastics Industry (SPI) are responsible for establishing uniform standards for glass and plastic container neck finishes. The closure industry does not necessarily adhere to the same standards, so it is often best practice to purchase containers and caps from the same manufacturer when possible.
“T” Dimension
The outside diameter of the thread. The tolerance range of the “T” dimension will determine the mate between bottle and closure.
“E” Dimension
The outside diameter of the neck. The difference between the “E” and “T” dimensions divided by two determines the thread depth.
“I” Dimension
The inner diameter of the bottle neck. Specifications require a minimum “I” to allow sufficient clearance for filling tubes. Linerless closures, with a plug or land seal, and dispensing plugs and fitments require a controlled “I” dimension for a proper fit.
“S” Dimension
Measured from the top of the finish to the top edge of the first thread. The “S” dimension is the key factor that determines the orientation of the closure to the bottle and the amount of thread engagement between the bottle and cap.
“H” Dimension
The height of the neck finish. Measured from the top of the neck to the point where the diameter “T”, extended down, intersects the shoulder.
Common GPI / SPI Neck Finishes

How to Measure a Neck Finish
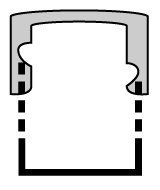
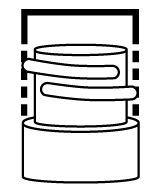
Cap Measurement and Bottle Measurement
To find a cap’s diameter, measure from one side of the inner wall to the opposite side. Calculate a bottle’s neck finish by measuring the diameter of the outermost threads. The resulting millimeter measurement will be the “T” dimension.
Then, see how many times the threads pass one another to determine the finish.
(ex. 24 mm “T” dimension with 1.5 thread turns = 24/410 neck finish)
Credit: sks-bottle.com
Posted in: Knowledge
Leave a Comment (0) →





























































 K.V.J. Union Company Limited
K.V.J. Union Company Limited